
Nowadays the most diverse libraries are used in SELEX experiments where highly variable initial nucleic acid pools of up to 10 15 individual sequences are employed.

Tatjana Schütze demonstrated emulsion PCR could be used in SELEX experiments for an unbiased amplification. Emulsion PCR amplification of complex gene libraries could prevent the absence of chinmeric products from happening. Emulsion PCR complex contains millions of cell-like compartments which are separated from each other without exchange of macromolecules, especially the PCR products ( Fig. Therefore, we proposed that product–product hybridization could be avoided if partition the reaction mixture into droplets, each of which is designed to contain only one template. They thought the most likely mechanism of this conversion is product–product hybridization rather than primer-primer hybridization. Furthermore, when the products reached maximum level, additional five cycles completely converted the products to by-product even though the primers were still present with certain concentration in the mixture, which leaded to the loss of potential high affinity and specificity apatamers and finally, even the failure of selection. Musheev's study showed that by-products appeared as early as the fifth cycle of PCR. However, during the PCR amplification stage, by-products formation inhibits the product generation and consequently limits the application of conventional PCR in apatamer selection.

Actually, efficient separation and amplification are both necessary for productive SELEX process. However, only few reported PCR amplification application in this area. Many studies showed that flow cytometry, capillary electrophoresis and other techniques are efficient methods for separation in apatamer selection –.
#BRIDGE PCR VS EMULSION PCR FREE#
For each round, it includes two stages: (1) separation of oligonucleotide-target complexes with free targets and non-bound oligonucleotides and (2) amplification of the bound sequences by polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The main strategy for obtaining aptamers is designated as SELEX (systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment) which consists of several rounds of sequence selection that bind to specific target molecules. Aptamers can be obtained in vitro by directed selection from libraries of random DNA sequences. In particular, aptamers are very attractive as a replacement for antibodies in diagnostics and treatment of diseases. These oligonucleotides fragments share most properties with monoclonal antibodies and have been showed that they successfully replaced antibodies in ELISA and Western blot, even smaller, more stable, and easier to be chemically synthesized compared with antibodies –. For instance, aptamers often bind to the functional parts of proteins and inhibit their activity. In addition, targets characteristics will be affected after binding. So, the results of our study indicated that emulsion PCR could improve the efficiency of SELEX.Īptamers are single-stranded DNA or RNA oligonucleotides capable of binding to other target molecules with high specificity, affinity and stability –. Furthermore, the concentration of the Taq DNA polymerase in the emulsion PCR mixture had a significant impact on product formation efficiency.
In addition, it also showed that the molecule ratio of template to compartment was crucial to by-product formation efficiency in emulsion PCR amplification. In emulsion PCR, we can completely avoid the product-product hybridization and avoid the most of primer-product hybridization if the conditions were optimized. Our results indicated that by-products in conventional PCR amplification were from primer-product and product-product hybridization.
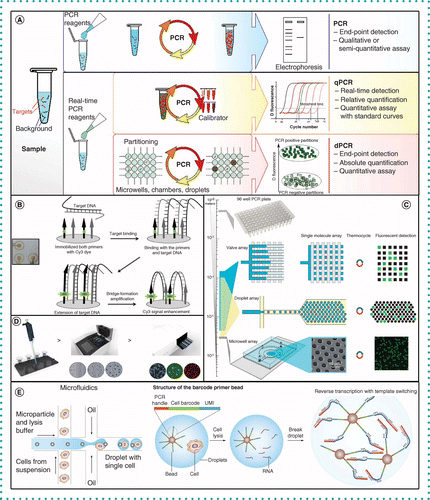
With this method, the by-products formation decreased tremendously to an undetectable level, while the products formation increased significantly. Here, we developed emulsion PCR for aptamer selection. Low efficiency is one of the limitations for conventional PCR amplification of random DNA sequence library in aptamer selection because of relative low products and high by-products formation efficiency. The main strategy to obtain aptamers is systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment (SELEX). Typically, they are selected from a large number of random DNA sequence libraries. Aptamers are short RNA or DNA oligonucleotides which can bind with different targets.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
